Hantavirus: What You Should Know!
Hantavirus: What You Should Know!
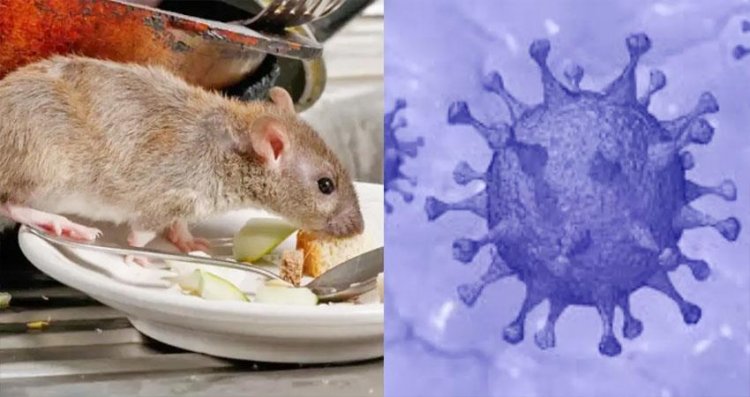
While the world is battling the pandemic of novel coronavirus, reports of a person in China dying due to a virus called ‘hantavirus’ have spread panic at such a difficult time. Here are a few facts about Hantavirus that one should know.
Hantaviruses are a family of viruses spread mainly by rodents and can cause varied disease syndromes in people worldwide. Infection with any hantavirus can produce hantavirus disease in people.
Hantaviruses causes 2 serious infections in humans:
- haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS)
- hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS)
Hantaviruses in the Americas are known as ‘New World’ hantaviruses and may cause hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS). Other hantaviruses, known as ‘Old World’ hantaviruses, are found mostly in Europe and Asia and may cause haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS).
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS)
Sin Nombre virus, the common cause of HPS in the USA, was discovered in 1993 following a cluster of acute and fatal illness in previously healthy adults. The cluster occurred in an area of the southwestern USA known as ‘Four Corners’. It was later established that the virus had caused human disease at least as early as 1959. By the end of 2012, a total of 617 cases of HPS had been reported in the United States. Thirty-five percent of all reported cases were fatal.
Haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS)
HFRS is a group of clinically similar illnesses occurring worldwide, and including Korean haemorrhagic fever, epidemic haemorrhagic fever. The incubation period is generally 2 to 4 weeks but can range from 2 days to 8 weeks.
Infection with these viruses can cause a disease characterised by fever, headache, gastrointestinal symptoms and renal dysfunction. The more severe forms of disease have haemorrhagic (bleeding) manifestations.
Transmission
Each hantavirus is specific to a different rodent host. Once infected the rodent will secrete infectious virus for prolonged periods, probably for life. Transmission of the virus to human occurs through the inhalation of infected animal excreta and fluids, such as urine, faeces and saliva
To help reduce the risk of infection, simple hygiene precautions such as washing your hands after handling rats or their bedding and cage should be applied.

Treatment for the virus
There is no specific treatment, cure, or vaccine for hantavirus infection. According to the US’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), “However, we do know that if infected individuals are recognised early and receive medical care in an intensive care unit, they may do better. In intensive care, patients are intubated and given oxygen therapy to help them through the period of severe respiratory distress.”
This news of the man getting infected has led some on social media to start panicking that another viral pandemic is ready to make the rounds, even as the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19 has infected at least 387,382 people across the globe, and killed 16,767 and counting.
The best thing you can do is eliminate contact with rodents at home, at work or at your campsite as much as you can. At home, seal up any holes or gaps in your house, apartment or garage that could let rodents in. Place traps in and around your home to combat any rodent infestation. And seal and clean up easy-to-get food.
Sanitation is the key. But, this is not what you should worry about right now as long as you are not surrounded by Rodents.
Let’s know the facts and spread them, not the myths!















































